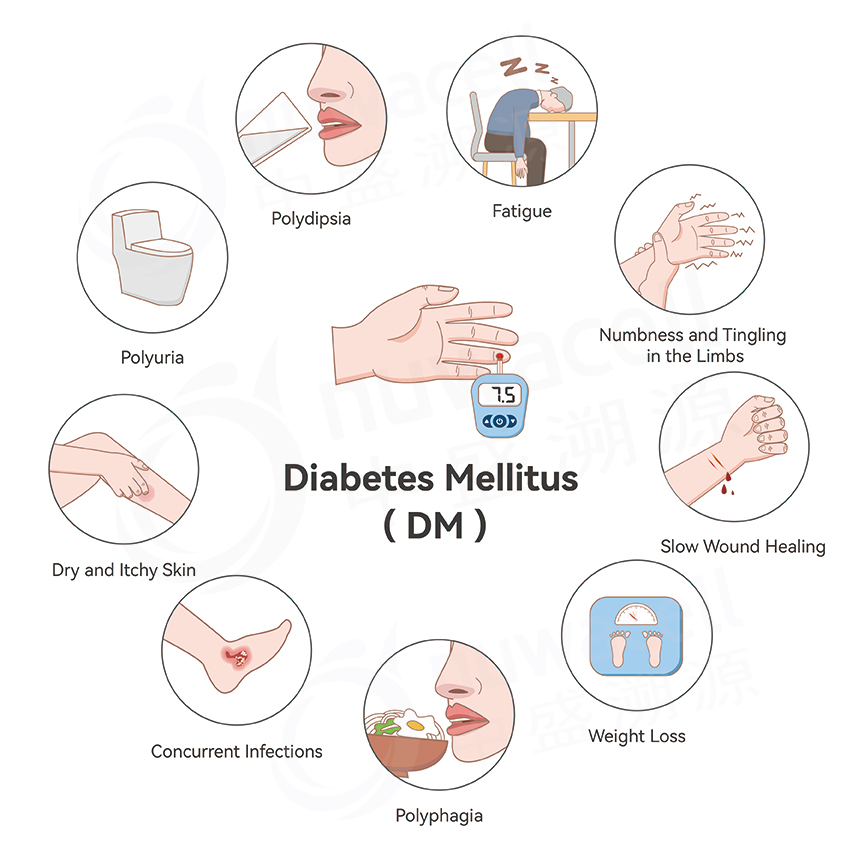
Diabetes Mellitus (DM) is a condition of hyperglycemia caused by impaired insulin secretion and varying degrees of insulin resistance. Early symptoms are associated with hyperglycemia and include polydipsia, polyuria, polyphagia, and blurred vision. Late-stage complications include angiopathy, peripheral neuropathy, nephropathy, and increased susceptibility to infections.
A study published in The Lancet reported that the global number of individuals with diabetes exceeded 500 million in 2021. This number is projected to double, surpassing 1.31 billion, within the next 30 years. China has the largest diabetic population worldwide. In recent years, the prevalence of diabetes among adults in China has continued to rise, reaching 11.9%, with an increasing trend of onset at younger ages.
Currently, insulin injection remains the primary treatment for patients with type 1 diabetes and those with advanced type 2 diabetes. Achieving a functional cure for diabetes has been a significant challenge in the field of regenerative medicine.
Islet transplantation or the generation of new islet cells using stem cell technology offers the potential to supplement or replace the lost insulin-secreting function in patients. This approach may enable patients to become independent of exogenous insulin, bringing new hope for a "cure" for diabetes.
Leveraging the unlimited expansion and directed differentiation capabilities of induced pluripotent stem cells (iPSCs), iPSCs can serve as a stable cell source for the large-scale production of batch-consistent, stable, and uniform islet cells. This method addresses issues such as limited donor availability and heterogeneity among donors.
|
iPSC-Derived Islet Progenitor Cell Therapy for DM
Through continuous technological innovation and optimization, Nuwacell has developed a high-purity, universal islet product, holding promise to achieve long-term control and even a complete cure for diabetes. |


 Overview
Overview Anti-inflammatory and Tissue Repair
Anti-inflammatory and Tissue Repair Regenerative Medicine
Regenerative Medicine Immunotherapy
Immunotherapy